Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Menthone® - 30gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 89-80-5
-
EINECS number : 201-941-1
-
FEMA number : 2667
-
FLAVIS number : 07.176
-
JECFA number : 429
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
Density : 0,895
-
Volatility : Head
-
Price Range : €€
Physico-chemical properties
-
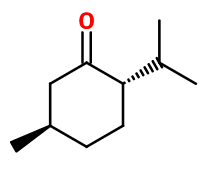
Molecular formula : C10H18O
-
Molecular Weight : 154,25 g/mol
-
Log P : 3,05
-
Fusion Point : -20°C
-
Boiling Point : 209°C
-
Detection Threshold : 170 ppb (0,000017%)
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : 79°C
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Menthone® is used in minty notes, for a deep and liquorice note. Allows to nuance the cold sensation of L-Menthol and L-Carvone in a mint reconstitution. Gives a very sweet and frosty mint effect.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Natural availability :
The natural production of Menthone® can be made from a dementholised Corn Mint EO (see L-Menthol).
Isomerism :
Menthone® is a mixture of two pairs of dextrorotatory and laevorotatory isomers: Menthone® and Isomenthone. Isomenthone has a more moldy smell than Menthone®. These two enantiomers have a strong tendency to interchange, making it difficult to separate them from synthetic Menthone® or from an essential oil. In the synthesis of Menthone®, the isomers of the molecules can be selected by changing the synthesis conditions or the starting reagent (for example, dehydrogenated or oxidized L-Menthol gives a mixture of L-Menthone® and D-isomenthone). Linalool, Nerol, Geraniol and Terpineol are some of the constitutional isomers of Menthone®. Nevertheless, they have a much more floral or terpenic smell, far from the frosty mint note of Menthone®.
Synthesis precursor :
Menthone® is a precursor to the synthesis of Menthol by catalytic hydrogenation, forming NeoMenthol and Menthol.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment

