Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
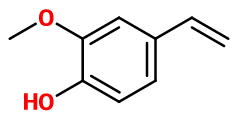
4-Vinyl Guaiacol
4-ethenyl-2-methoxyphenol ; 4-hydroxy-3-methoxystyrene ; 3-methoxy-4-hydroxystyrene ; 2-methoxy-4-ethenylphenol ; 2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol ; Ortho-methoxy-para-vinylphenol ; Varamol 106 ; Ortho-methoxy-para-vinylcathecol ; 4-vinylguaiacol

Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
VINYL GAIACOL | M_0063051 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 7786-61-0
-
EINECS number : 232-101-0
-
FEMA number : 2675
-
FLAVIS number : 04.009
-
JECFA number : 725
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
Density : 1,11
-
Volatility : Heart
-
Price Range : €€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Molecular formula : C9H10O2
-
Molecular Weight : 150,18 g/mol
-
Log P : Donnée indisponible.
-
Fusion Point : Donnée indisponible.
-
Boiling Point : 224°C
-
Detection Threshold : 1 à 3 ppb (0,0000003%)
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : 113°C
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
4-Vinyl Guaiacol, although used in aromas, can be used in balsamic, spicy, woody and leathery notes in perfumes, for a warm and spicy effect, close to Clove Bud EO, in association with Gaiac Wood EO.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Natural availability :
4-Vinyl Guaiacol is found in numerous current food products (tobacco, coffee and grapes for example), but is over all produced on a natural state thanks to ferulic acid, converted into 4-Vinyl Guaiacol during the alcoholic fermentation of some cereals, including corn. Thus, it can be extracted from it.
Isomerism :
4-Vinyl Guaiacol is used in perfumery for its note and structure close to Gaiac Wood EO and Eugenol. No other positional isomer of this molecule is used in this area. This molecule is a constitutional isomer of Benzyl acetate and Para-Cresyl acetate, but does not share the same olfactive family as these ingredients.
Synthesis precursor :
4-Vinyl Guaiacol is not a precursor for the synthesis of another olfactive compound.
Synthesis route :
4-Vinyl Guaiacol is synthesized in three steps starting from Vanillin. The first step consists in reacting it with acetic anhydride and sodium acetate, forming 3-methoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid, after an acidic hydrolysis. The last step consists in heating this intermediairy product, reacting it with quinoleine and hydroquinone, to decarboxylate the molecule and recover the final product : 4-Vinyl Guaiacol.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment

