Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
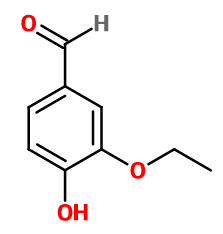
Ethyl vanillin
3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde ; Bourbonal ; Ethavan ; Ethovan ; 3-ethoxy protocatechualdehyde ; 2-ethoxy-4-formyl phenol ; 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde ; 3-ethoxy-4-oxidanylbenzaldehyde ; Ethyl protal ; Ethyl protocatechualdehyde-3-ethyl ether ; Ethyl protocatechuic aldehyde ; Ethylprotal ; Ethylprotocatechuic aldehyde ; Ethylvanillin ; 4-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde ; Quantrovanil ; Rhodiarome ; Rhodiascent ; Vanirome

Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Ethyl Vanilline - 30 Gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 121-32-4
-
EINECS number : 204-464-7
-
FEMA number : 2464
-
FLAVIS number : 05.019
-
JECFA number : 893
-
Appearance : White solid
-
Density : 1,186
-
Volatility : Base
-
Price Range : €€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Molecular formula : C9H10O3
-
Molecular Weight : 166,17 g/mol
-
Log P : Donnée indisponible.
-
Fusion Point : 76°C
-
Boiling Point : 295°C
-
Detection Threshold : 0,1 ppm (0,00001%)
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : 145°C
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Ethyl Vanillin is used in vanillic and fruity notes, often in association with Vanillin, in smaller proportions, as it is a more powerful product.
Year of discovery :
1894
Natural availability :
Ethyl Vanillin is not available in its natural state.
Isomerism :
Ethyl Vanillin does not have any isomer used in perfumery.
Synthesis precursor :
Ethyl Vanillin may undergo acetalization reactions in the presence of various alcohols or diols. It can also undergo esterification reactions in the presence of carboxylic acids.
Synthesis route :
Ethyl Vanillin synthesis can follow a similar pathway to Vanillin synthesis, starting from Guaethol rather than Guaiacol. A first step consists in reacting Guaethol with glyoxylic acid, at room temperature, in a basic medium and with a slight excess of Guaethol. A catalytic air oxidation of the intermediate product, followed by a decarboxylation in an acidic medium, releasing CO2, allows to obtain Ethyl Vanillin.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment

