Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
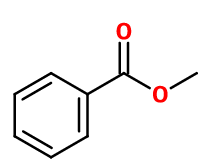
METHYL BENZOATE | M_0050654 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 93-58-3
-
EINECS number : 202-259-7
-
FEMA number : 2683
-
FLAVIS number : 09.725
-
JECFA number : 851
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
Density : 1,086
-
Volatility : Head/Heart
-
Price Range : €
Physico-chemical properties
-
Molecular formula : C8H8O2
-
Molecular Weight : 136,15 g/mol
-
Log P : 2,2
-
Fusion Point : -15°C
-
Boiling Point : 200°C
-
Detection Threshold : 110 ppb (0,000011%)
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : 77°C
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Methyl Benzoate is used in white floral notes such as ylang-ylang, jasmine, tuberose, mimosa or leather and cinnamic notes.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Natural availability :
Methyl Benzoate is especially present in Ylang-Ylang Extra EO (and other ylang fractions), from which it can be extracted in its natural state.
Isomerism :
Phenylacetic Acid and Anisic Aldehyde are constitutional isomers of Methyl Benzoate. Their smell is however very different.
Synthesis precursor :
Methyl Benzoate is a major intermediate in the synthesis of Polyethylene Terephtalate (PET), which is the plastic that we consume every day.
Synthesis route :
The synthesis of Methyl Benzoate can be made by esterification between benzoic acid and methanol, by acid catalysis.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment

