Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Do you sell any of the raw materials? Would you like to let our users know?
Send an email to fournisseurs@scentree.coto learn about our advertising opportunities.
Do you sell any of the raw materials? Would you like to let our users know?
Send an email to fournisseurs@scentree.coto learn about our advertising opportunities.
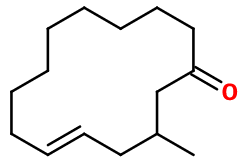
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 259854-70-1
-
EINECS number : 452-280-2
-
FEMA number : Donnée indisponible.
-
FLAVIS number : Donnée indisponible.
-
JECFA number : Donnée indisponible.
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
Density : 0,93
-
Volatility : Base
-
Price Range : €€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Molecular formula : C15H26O
-
Molecular Weight : 222,37 g/mol
-
Log P : 5,6
-
Fusion Point : Donnée indisponible.
-
Boiling Point : 258°C
-
Detection Threshold : 0,1 ng/l air
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : >93°C
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Cosmone® is generally used as a nitromusk replacer. It has a quite similar effect and makes it possible to nuance base notes, thanks to its fruity and green facets.
Year of discovery :
Discovered in 1998
Natural availability :
Cosmone® does not exist on a natural state. Thus, it can't be used as extracted from a plant.
Isomerism :
Cosmone® has two diastereisomers, trans and cis. In perfumes, a blend of these two isomers is used, because they do not have a strong olfactive difference. Cosmone® is initially a blend of two positional isomers, called Cosmone® I and II. Both are obtained during the synthesis, and can be separated by distillation. Cosmone® is a constitutional isomer of some sandalwood alcohols as Javanol® or Polysantol®. Nevertheless, they do not have any olfactive similarities.
Synthesis precursor :
Cosmone® is not used for the synthesis of another molecule of olfactive interest.
Synthesis route :
Cosmone® is synthesized by a Wittig reaction in an alkaline medium, involving (4-carboxy-3-methylbutyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide and methyl 9-oxononanoate. This frist step leads to an ester, esterified using methanol (catalysor : paratoluensulfonic acid). Putting the ester in contact with pure sodium leads to a Bouveau-Blanc rearrangement, cycling the intermediary product into two acetates, linked by a positional isomery. To remove the ester groups from these two molecules, a reductive deacetoxylation is carried out with ammonia and calcium. This way, both Cosmone® isomers are obtained, to be separated by distillation.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment

