| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Huile essentielle de Ciste - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
CISTE | N0300 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | - |
|
|
CISTE | B275 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | - |
|
|
CISTE | F0860 |
Visit website
|
Huile essentielle |

|
- | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 8016-26-0
-
EINECS number : 89997-74-0
-
FEMA number : 2608
-
Appearance : Yellow liquid
-
Density : 0,895 - 0,945 @20°C
-
Volatility : Base
-
Price Range : €€€€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value :
-
Flash Point :
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Used in all types of perfumes, for amber, chypre and fougere notes. Used to support floral notes.
Major Components :
- Viridiflorol (10 - 15%)
- Delta-cadinene (≈3%)
- Camphor (≈3%)
- Bornyl acetate (≈2%)
- Cubenol (≈2%)
- Plotter(s) : Ethyl phenylpropanoate (≈0,1%)
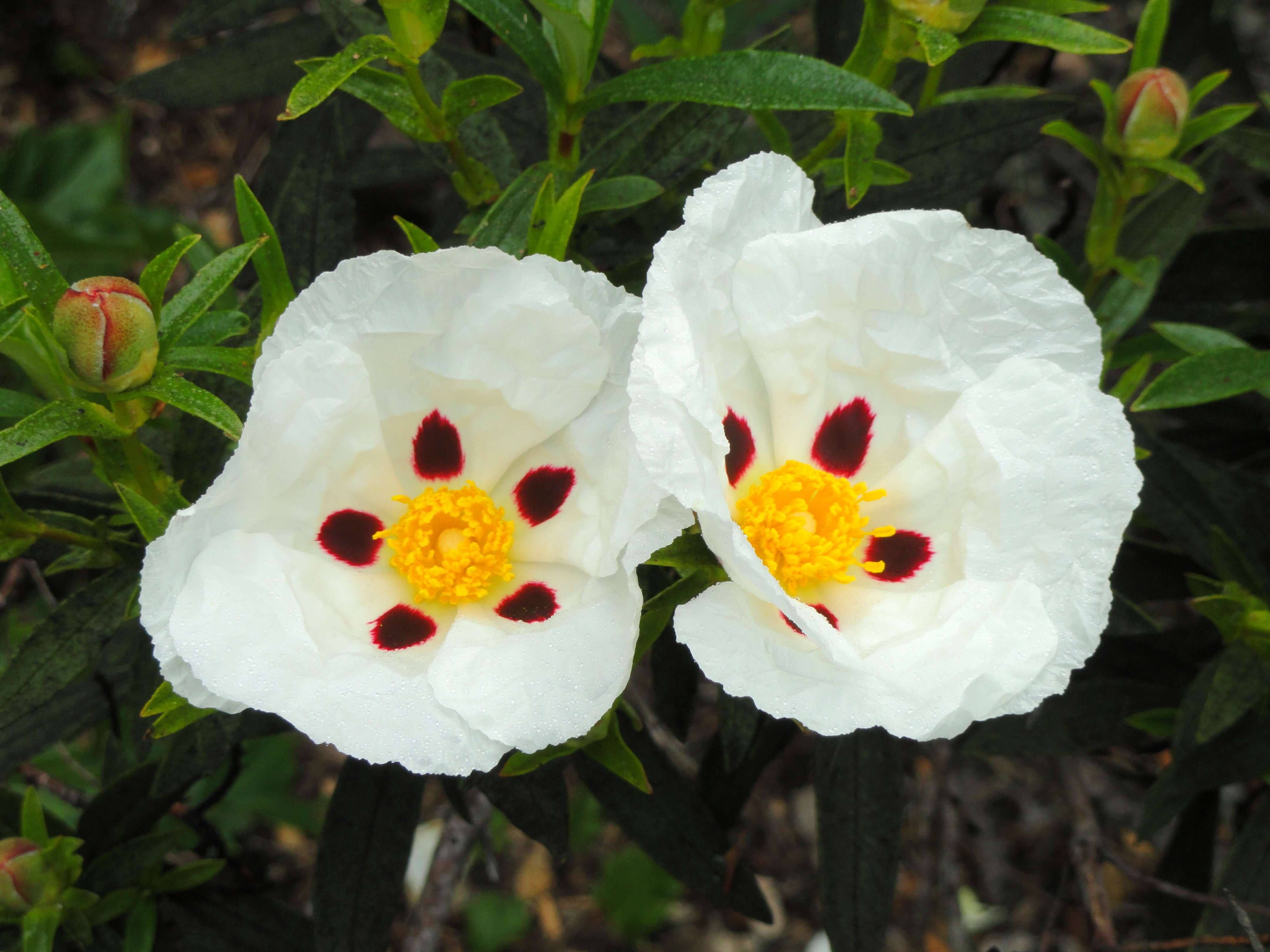
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Botanical name :
Cistus ladanifer L.
Synonyms : Cistus ladaniferus L. // Cistus ladanifer f. immaculatus Dans.
Botanical profile :
The cistus belongs to the Cistaceae family and to the genus Cistus.
Chemotypes :
The genus Cistus includes about 20 different species, the majority of which exudes fragrant gum.
Among these, the most used are:
Cistus ladaniferus var. albiflorus, var. maculatos, var. stenoiphyllus, which produce the resin used in perfumes.
Cistus creticus, with rose to purple petals, surronding a tuft of stamens.
Cistus salvifolius, with white petals.
Cistus parviflorus, with pale rose petals.
Extraction process :
In April, Cistus ladaniferus fields are covered with the famous white flowers, but they don't smell and are very delicate (they only last a few days). It is necessary to wait a few months, around May-June, for a new shoot to appear. This new branch protects itself from the sun - and from the summer heat of southern Spain - by secreting a very fragrant viscous gum. We use the latter in perfumery.
In July, from dawn to noon, new branches are cut with a sickle, bundled and taken to the factory to extract the gum. It will then be necessary to wait another 3 years to harvest the cistus again.
The branches and twigs of the shrub are also used to obtain the essential oil. They are dried and immersed in a bath of boiling water to exude the oils and collect them on the surface. The plant can also be extracted by steam distillation to obtain an essential oil after a few hours of extraction, with a yield of 6 to 7 ‰ for a Spanish cistus and up to 1 ‰ for a French cistus.
Other comments :
Cistus is a shrub about two meters high, with pink, red or white flowers depending on the variety.
Cistus harvesting on an industrial scale was first done in the region of Salamanca, and was then exported to the South of Spain, along Portugal, to Andalusia, vers the greatest cultures in Europe can be found.
Bases are obtained by deriving ciste-labdanum: Dynamone is obtained by cracking (breaking bonds of heavier molecules) and Ambrarome Absolute is obtained by pyrogenation among others.
The essential oil is more powerful, rising and terpenic but less ambered, warm and resinous than the absolute. The absolute is also cheaper than the essential oil.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment

