Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Do you sell any of the raw materials? Would you like to let our users know?
Send an email to fournisseurs@scentree.coto learn about our advertising opportunities.
Do you sell any of the raw materials? Would you like to let our users know?
Send an email to fournisseurs@scentree.coto learn about our advertising opportunities.
General Presentation
-
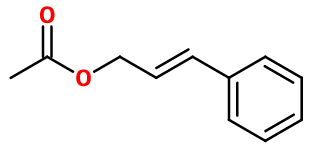
CAS N° : 103-54-8
-
EINECS number : 203-121-9
-
FEMA number : 2292
-
FLAVIS number : 09.018
-
JECFA number : 650
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
Density : 1,053
-
Volatility : Heart
-
Price Range : €€
Physico-chemical properties
-
Molecular formula : C11H12O2
-
Molecular Weight : 176,22 g/mol
-
Log P : 2,9
-
Fusion Point : Donnée indisponible.
-
Boiling Point : 264°C
-
Detection Threshold : Donnée indisponible.
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : 118°C
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Cinnamyl acetate is used in reproductions of hyacinth, rosy and woody-spicy notes, to provide a green and balsamic effect.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Natural availability :
Cinnamyl acetate can be found in small quantity in some plant extracts such as Ylang-Ylang Extra EO (and other ylang fractions), Laurel EO and Cinnamon Leaf EO, as well as Narcissus Absolute, among others.
Isomerism :
Cinnamyl acetate has two diastereoisomers, due to the presence of a double bond in its structure. The (E) isomer of Cinnamyl acetate has an even sweeter smell than the (Z) isomer. Anyway, both have a similar smell, which explains the use of a racemic mixture of the two isomers in perfumery.
Synthesis precursor :
Cinnamyl acetate is not a precursor of the synthesis of another compound of olfactive interest.
Synthesis route :
Cinnamyl acetate is synthesized by an esterification reaction between Cinnamyl Alcohol and acetic acid. This reaction is catalyzed by the presence of a small quantity of a strong acid such as sulphuric acid. In addition, the yield of this reaction can be improved by the use of acetic anhydride or chloroacetic acid, rather than acetic acid.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is not restricted for the 51th amendment

