Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
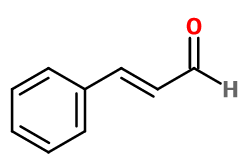
CINNAMIC ALDEHYDE | M_0050621 |
Visit website
|
Naturel | - | - | - | - | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 104-55-2
-
EINECS number : 203-213-9
-
FEMA number : 2286
-
FLAVIS number : 05.014
-
JECFA number : 656
-
Appearance : Viscous yellow liquid
-
Density : 1,05
-
Volatility : Heart/Base
-
Price Range : €
Physico-chemical properties
-
Molecular formula : C9H8O
-
Molecular Weight : 132,16 g/mol
-
Log P : Donnée indisponible.
-
Fusion Point : -7,5°C
-
Boiling Point : 248°C
-
Detection Threshold : 50 et 750 ppb (0,000075%)
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : 71°C
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Cinnamaldehyde gives a spicy note to fruity and oriental accords.
Year of discovery :
Discovered en 1856.
Natural availability :
Cinnamaldehyde is present in a large quantity in Cassia EO (about 90%) and Ceylon Cinnamon EO (about 75%). It can therefore be extracted from these essential oils by fractional distillation.
Isomerism :
Like Cinnamyl Alcohol, Cinnamaldehyde can be divided into two diastereoisomers: trans or cis. Trans is the most found in nature. Both have a cinnamon-like smell, but the trans is warmer and smells even more like cinnamon than cis. The raw material used in perfumery is usually a mixture of the two isomers.
Synthesis precursor :
Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde provides DihydroCinnamaldehyde and DihydroCinnamyl Alcohol. Moreover, the oxidation of the aldehyde gives a Cinnamic Acid, another compound of olfactory interest. Finally, Cinnamaldehyde forms a Schiff base by reaction with Methyl Anthranilate or Indole for example.
Synthesis route :
The synthesis of Cinnamaldehyde is made by a condensation of Benzaldehyde with Acetaldehyde, using an excess of Benzaldehyde and gradually adding Acetaldehyde, in order to avoid self-condensation of the latter.
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A B C DCat.6 0,045 % 0,014 % 0,021 % 0,25 % 0,064 % 0,042 % 0,064 % 0,014 %0,15 % Cat.5A B C DCat.6 0,064 % 0,042 % 0,064 % 0,014 %0,15 % Cat.7A BCat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A BCat.11A BCat.12 0,17 % 0,17 %0,014 % 0,49 % 0,49 % 1,8 %0,014 % 0,014 %No Restriction Cat.10A BCat.11A BCat.12 0,49 % 1,8 %0,014 % 0,014 %No Restriction
Annexe I :
Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Botanical Name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Cinnamon bark oil, Laos | Cinnamomum loureiroi Nees | 97659-68-2 | 95 |
| Cinnamon bark CO2 extract | Cinnamomum verum J. Presl syn. C. zeylanicum Blume | 8015-91-6 | 77,5 |
| Cinnamon bark oil | Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume | 8015-91-6 | 75 |
| Cinnamon leaf oil | Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume | 8015-91-6 | 1,5 |
| Cassia bark oil | Cinnamomum cassia [L.] J. Presl syn. C. aromaticum Nees | 8007-80-5 | 78,85 |
| Cassia bark oleoresin | Cinnamomum cassia [L.] J. Presl syn. C. aromaticum Nees | 8007-80-5 | 46,23 |
| Cassia oil | Cinnamomum cassia [L.] J. Presl syn. C. aromaticum Nees | 8007-80-5 | 79,5 |
| Styrax extract | Liquidambar spp. | 8046-19-3 | 0,05 |
| Styrax oil | Liquidambar styraciflua L. | 8046-19-3 | 0,03 |
| Styrax oil, Honduras | Liquidambar styraciflua L. | 8046-19-3 | 0,1 |
| Styrax resinoid | Liquidambar styraciflua L. | 8046-19-3 | 0,04 |
| Hyacinth absolute | Hyacinthus orientalis L. | 8023-94-7 | 0,3 |
| Benzoin resinoid, Siam | Styrax tonkinensis (Pierre) Craib ex Hartwick | 0,01 | |


