| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Naturality | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | Certifications | Comments | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
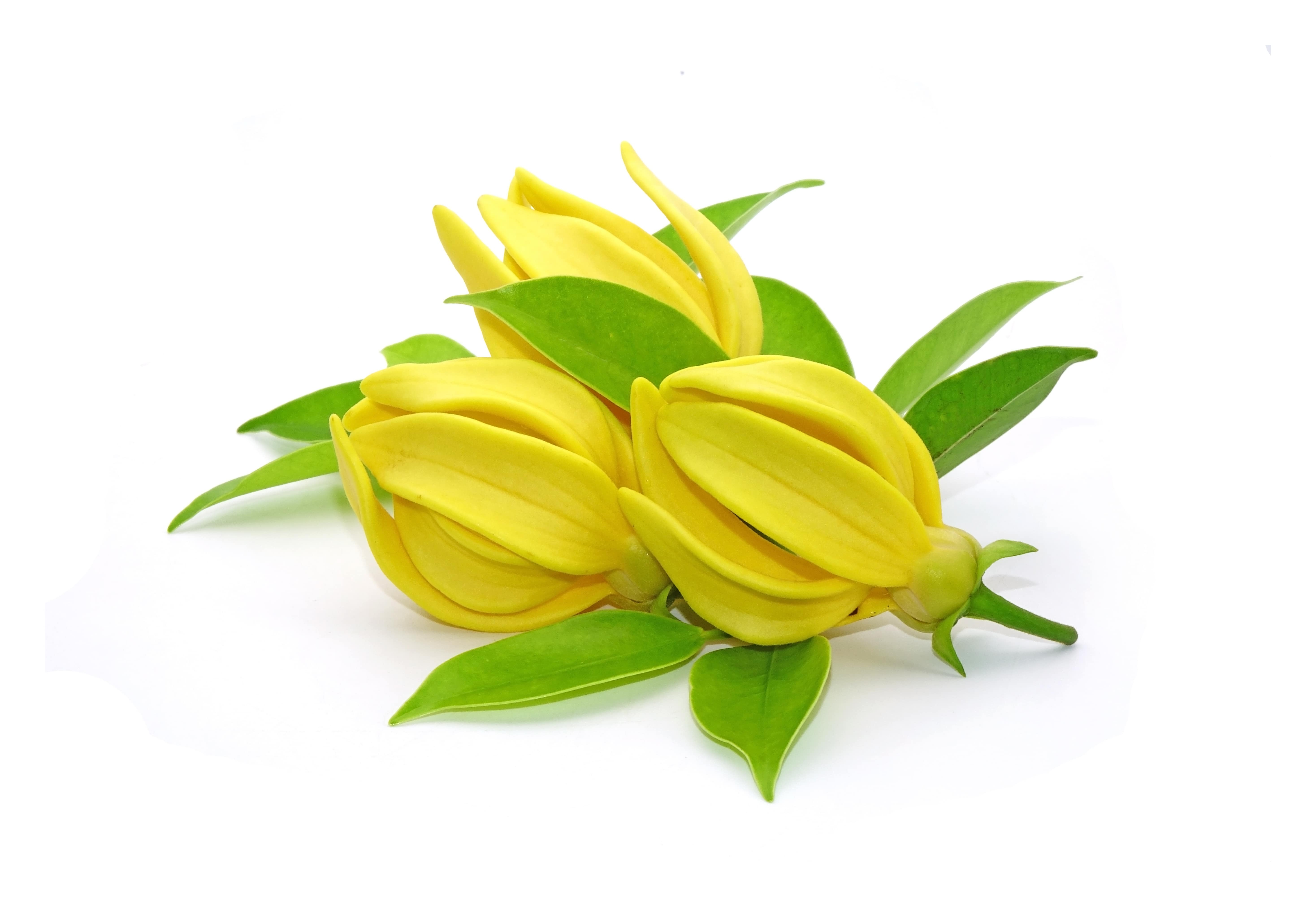
YLANG | P00554161000 | Absolue | - | Cananga odorata (Lam.) Hook.f. & Thomson | Fleur | Madagascar | more | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 8006-81-3
-
EINECS number : 83863-30-3
-
FEMA number : 3119
-
Density :
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : Linalool - Benzyl Benzoate
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Heart
-
Price Range : €€€€
-
Appearance : Green liquid
Uses
Other comments :
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
The esters identified in this raw material can form their corresponding acid in stability tests
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Uses in perfumery :
Data not available.
Major Components :
Data not available.
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Botanique :
The ylang-ylang is the flower of a tree of the Annonaceae family and the genus Cananga.
Chemotypes :
Ylang has another similar specie, also used in perfumery, but in smaller quantities: Cananga genuina.
There is also the Cananga macrophylla, widespread in Indonesia, which gives the Cananga EO, by hydrodistillation. This essential oil has a lower quality and is less expensive.
Finally, there are four main ''false ylang '' that also belongs to the Annonaceae family :
The Harachampala (Artabotrys Hexapetalus), grown in India and Sri Lanka. The grains of selim, a Guinean and Ethiopian pepper (Xylopia aethiopica), whose flowers give an essential oil with Eucalyptol.
The Monkey pepper (Xylopia aromatica).
The Monodora citriodora which provides a Citral essential oil.
Extraction process :
The Canaga odorata is a tree that can measure 20 to 30 meters in height. To facilitate the harvest of the flowers, the trees are topped at two meters height throughout their life. In addition, each branch, called ''epicormic shoot '', is cut to stress the tree so it produces a maximum of flowers to ensure the sustainability of it specie. The branches fall back to the ground, and flowers are found under the leaves. Green at first, then yellow when ripe.
The ylang-ylang flower is cultivated all year long in a tropical or sub-tropical climate (flowering is more abundant from November to April). At maturity, the base of the flowers turns red. The harvest is done in the morning, from 5am to 8am, to prevent the evaporation of the aromatic molecules of the flower during the day. The harvest is done manually by women and the flowers are collected in baskets (5 kg of flowers per hour, knowing that a flower weighs no more than two grams!) and weighed at the factory.
During the same day, the flowers are subjected to a steam distillation. This means that the most volatile molecules are collected in the very first fraction called ''Extra '', followed by fraction I, II and III. The flower can also be totally distilled in a single fraction, called ''complete essential oil ''.
The extraction of ylang-ylang often turns around 2%, regardless of its fractionation. An adult tree can produce 10 to 20 kg of flowers per year.
It is finally possible to extract the flowers with a volatile solvent, to obtain a concrete and an absolute. No fractionation is possible with this process.
Ylang-ylang essential oils can be rectified by distillation to remove insoluble compounds.
Geographic origin :
Data not available.
Regulations & IFRA
-
IFRA 51th : This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
-
Restriction type : RESTRICTION
-
Cause of restriction : DERMAL SENSITIZATION
-
Amendment : 49
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A Cat.5B Cat.5C Cat.5D Cat.6 0,13 % 0,039 % 0,78 % 0,73 % 0,18 % 0,18 % 0,18 % 0,18 % 0,43 % Cat.7A Cat.7B Cat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A Cat.10B Cat.11A Cat.11B Cat.12 1,5 % 1,5 % 0,077 % 1,4 % 5,1 % 5,1 % 2,8 % 2,8 % No Restriction
Annexe I :
Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,5 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,5 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,5 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,5 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,3 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 1 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,3 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 1 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,5 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,5 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,5 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,5 |
| Benzyl salicylate | 118-58-1 | 3 |
| Benzyl salicylate | 118-58-1 | 3 |
| Benzyl salicylate | 118-58-1 | 4 |
| Benzyl salicylate | 118-58-1 | 3 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 4,2 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 2 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 1,5 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 3 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 4,5 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 7 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 7 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 6 |
| Farnesol | 4602-84-0 | 1,4 |
| Farnesol | 4602-84-0 | 2 |
| Farnesol | 4602-84-0 | 1,5 |
| Farnesol | 4602-84-0 | 1,5 |
| Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0,1 |
| Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0,2 |
| Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0,05 |
| Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0,5 |
| Farnesal | 19317-11-4 | 0,02 |
| Farnesal | 19317-11-4 | 0,02 |
| Benzyl cyanide | 140-29-4 | 0,05 |
| Benzyl cyanide | 140-29-4 | 0,02 |
| Benzyl cyanide | 140-29-4 | 0,02 |
| Benzyl cyanide | 140-29-4 | 0,03 |

