Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Naturality | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | Certifications | Comments | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Rose Oxide - 30 Gr | - | - | - | - | - | - | more | - | |
|
|
Rose Oxide 70 | 30365220 | Molecule | - | - | - | - | more | - | |
|
|
Rose Oxide 90 | 30365218 | Molecule | - | - | - | - | more | - | |
|
|
Rose Oxide 90 BMBcert™ | 30785436 | Molecule | - | - | - | - | more | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 16409-43-1
-
EINECS number : 240-457-5
-
FEMA number : 3236
-
Density : 0,875
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Head
-
Price Range : €€€
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
FLAVIS number : 13.037
-
JECFA number : 1237
Information on synthetic ingredients
-
Acid Value : Lorem Ipsum
-
Boiling Point :
-
Detection Threshold : Donnée indisponible.
-
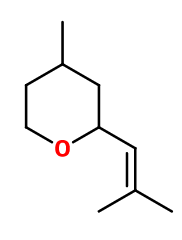
Molecular formula : C10H18O
-
Log P : 3,3
-
Molecular Weight : 154,25 g/mol
-
Fusion Point : <-100°C
-
Flash Point : 70°C
-
Vapor pressure : Lorem Ipsum
Uses
Other comments :
Comparing it to other green and rosy notes, Rose Oxide does not have such metallic notes as Diphenyl Oxide or Benzophenone.
Stability :
Stable in perfumes and diverse functional bases
Uses in perfumery :
Rose Oxide is used in rose reconstitutions, to bring the greeny flower stem note. Also used in geranium notes, for a fruity nuance. Contributes to a raw vegetable side, and enhances fruity note of litchi, exotic and red fruits.
Year of discovery :
Discovered in 1961 by scientists Casimir Seidel and Max Stoll.
Isomerism :
There are two enantiomers of Rose Oxide, whose synthesized proportion may vary depending on the synthesis parameters. Dextrorotatory Rose Oxide is spicier when the laevorotatory enantiomer is more metallic. Both enantiomers are often used separately in perfumes. Linalool, Geraniol and Eucalyptol are among the constitutional isomers of Rose Oxide. Their smell is however very different, whether it is floral-fresh, rosy or camphorated.
Synthesis precursor :
Rose Oxide is not a precursor to the synthesis of another compound of olfactory interest.
Natural availability :
The natural Rose Oxide is present in Damask Rose EO (and other roses) and can be extracted from it.
Synthesis route :
Rose Oxide is synthesized from Citronellol. The chosen enantiomer of Citronellol guides the enantiomeric form of the final product. A photo-oxidation is carried out on Citronellol to synthesize the two allylic hydroperoxides associated with this molecule. The two corresponding diols are obtained by a catalytic hydrogenation. Finally, the two compounds are put in an acid medium (with dilute sulfuric acid for example) in order to obtain a mixture of the two possible isomers of Rose Oxide. The unreacted diols are separated from the reaction medium by a fractional distillation. Using dextrorotatory Citronellol for this synthesis yields a 7 : 3 mixture of the cis : trans isomers of Rose Oxide. If the dehydration step is carried out with a stronger acid, an even greater proportion of cis isomer can be obtained. Another synthetic route consists of several stages of halogenation and dehalogenation of Citronellol.
Regulations & IFRA
This ingredient is not restricted

