Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 103-45-7
-
EINECS number : 203-113-5
-
FEMA number : 2857
-
Density : 1,033
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Heart
-
Price Range : €
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
FLAVIS number : 09.031
-
JECFA number : 989
Information on synthetic ingredients
-
Acid Value : Lorem Ipsum
-
Boiling Point : 239°C
-
Detection Threshold : 40 à 200 ppb (0,00002%)
-
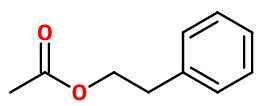
Molecular formula : C10H12O2
-
Log P : 2,27
-
Molecular Weight : 164,2 g/mol
-
Fusion Point : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : 105°C
-
Vapor pressure : Lorem Ipsum
Uses
Other comments :
The esterification of Phenyl Ethyl Alcohol brings a more fruity and even more honeyed smell to the reaction product. This is often the role of esters in perfumery: to bring a fruity note, while keeping a backnote of the corresponding alcohol. Here, the fruity note is close to pear.
Stability :
acetates may form acetic acid in stability.
Most of the time, the presence of an aromatic cycle in a molecule brings coloration through time.
Uses in perfumery :
Phenyl ethyl acetate is used in addition to phenyl ethyl alcohol, for its even more honeyed and fruity note, in reconstitutions of rose or lilac.
Year of discovery :
Data not available.
Isomerism :
Phenyl Ethyl acetate has several constitutional isomers used in perfumery. These include Styrallyl acetate, from which one of the carbons in the main chain is ramified, and which has a much more fruity and green smell, reminiscent of rhubarb. Finally, there is Benzyl Propionate, whose esterified chain is longer than the chain linked to the aromatic cycle, to get a more fruity smell of pear and jasmine.
Synthesis precursor :
Phenyl Ethyl acetate is not a precursor to the synthesis of another compound of olfactory interest.
Natural availability :
Phenyl ethyl acetate is present in small quantity in several commonly used extracts: Ylang-Ylang Extra EO (and other ylang fractions), Narcissus Absolute, Indian Geranium EO, Champaca Absolute, and in several consumer products such as liquors. It can be extracted in its natural state from the above-mentioned extracts.
Synthesis route :
Phenyl Ethyl acetate can be synthesized by an esterification reaction between Phenyl Ethyl Alcohol and acetic acid, in the presence of a catalyst such as concentrated sulfuric acid, in small quantity in the reaction medium. The yield of this reaction can be improved by using acetic anhydride or chloroacetic acid instead of acetic acid.
Regulations & IFRA
This ingredient is not restricted

