General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 8021-36-1
-
EINECS number : 639-660-5
-
FEMA number : Donnée indisponible.
-
Density :
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : Cinnamates
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Base
-
Price Range : €€€
-
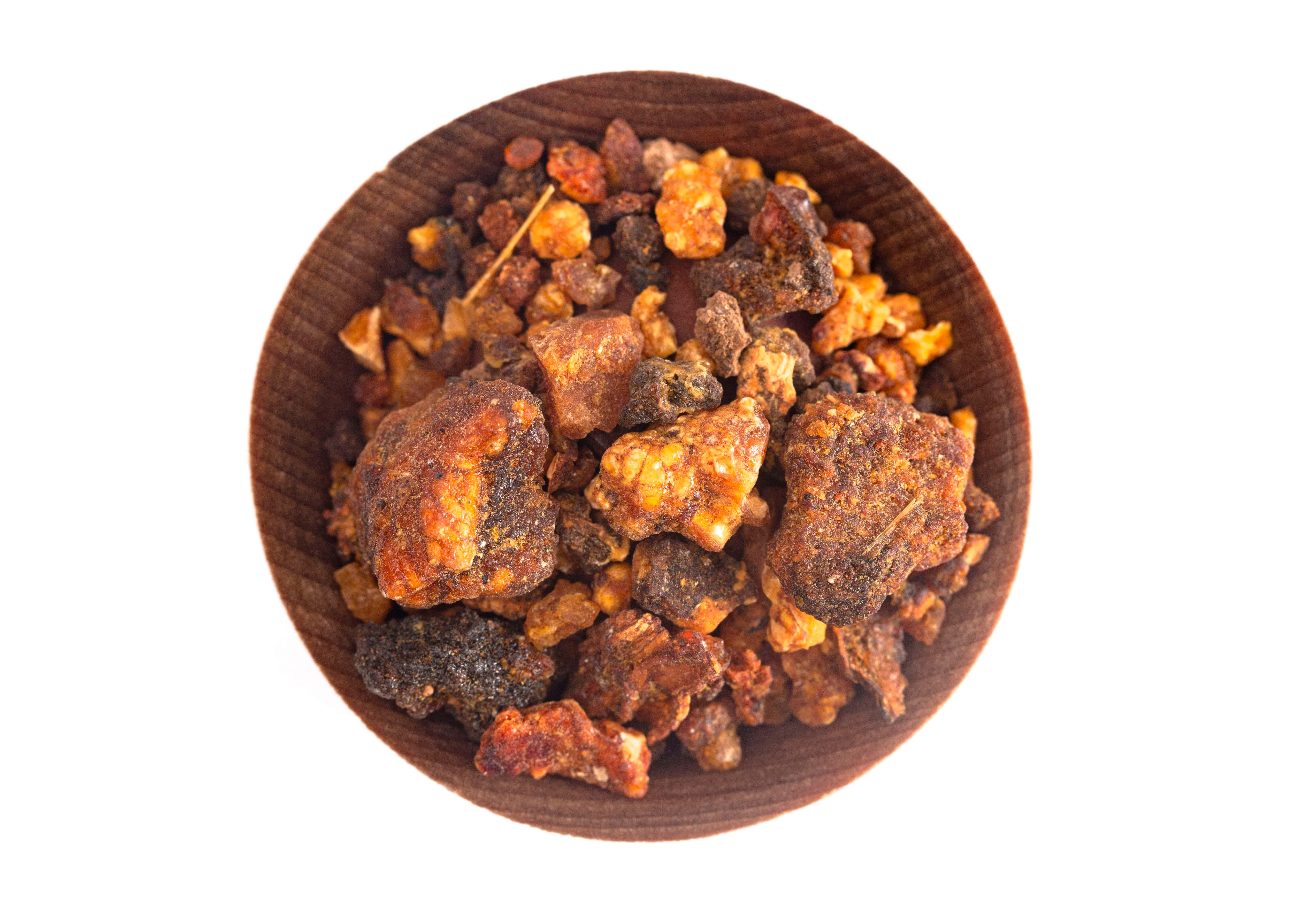
Appearance : Amber to brown resin
Uses
Other comments :
Originally, opoponax was one of the resins that were burned for the gods because the fumigations are smellious and considered as an offering in this regard.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Uses in perfumery :
Used in all types of perfumes, in chypre, oriental, woody and incense notes. Provides warmth, hold and trail. Good fixator.
Major Components :
- Elemene
- Capene
- Sesquiterpenes and furanic sesquiterpenones
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Botanique :
Opoponax is the resin of a tree of the Burseraceae family and the genus Commiphora.
Chemotypes :
The genus Commiphora regroups 190 species. In perfumery, Commiphora myrrha is also cultivated, and corresponds to myrrh resinoid or myrrh EO, also grown in East Africa but with a spicier and reminiscent smell of plastic.
Extraction process :
As for myrrh, the resin secretion of the opoponax tree is provoked to let the resin tears flow down the bark of the tree. Once dry, these tears are collected with a blade and freed from their impurities by filtration. After that, they are exported to Europe to be extracted.
A resinoid can be obtained by the extraction of the resin with alcohol. Thanks to the alcohol, the waxes precipitate out of the resin and the fragrant principle remains after a glazing at 32 °F and a filtration, without any further reprocessing.
An essential oil is obtained by hydrodistillation of the resin. It is also possible to obtain a supercritical CO2 extract of myrrh with a superior olfactory quality.
The resinoid may be bleached by distillation.
Geographic origin :
Data not available.
Regulations & IFRA
This ingredient is not restricted


