Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Naturality | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | Certifications | Comments | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Muscone - 30 Gr | - | - | - | - | - | - | more | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 541-91-3
-
EINECS number : 208-795-8
-
FEMA number : 3434
-
Density : 0,922
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Base
-
Price Range : €€€€
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
FLAVIS number : 07.111
-
JECFA number : 1402
Information on synthetic ingredients
-
Acid Value : Lorem Ipsum
-
Boiling Point : 130°C (à 0,66 hPa)
-
Detection Threshold : 9,8 ppb (0,00000098%)
-
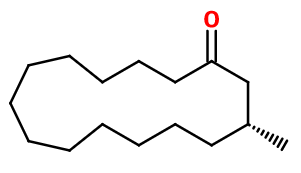
Molecular formula : C16H30O
-
Log P : 6,6
-
Molecular Weight : 238,4 g/mol
-
Fusion Point : Donnée indisponible.
-
Flash Point : >100°C (>212°F)
-
Vapor pressure : Lorem Ipsum
Uses
Other comments :
Muscone® is less powerful than Muscenone®, with a similar structure.
Muscone® is the first non-nitrated musk to appear on the market. Initially extracted from Musk Tonkin (some qualities of which contain up to 20%). It took 20 years for chemists to succeed in unlocking the secret of its molecular structure. Indeed, at the beginning of the 20th century it was difficult to imagine that a molecule could have more than 6 carbons in its cycle. It was therefore necessary to wait for the arrival of more advanced analytical techniques to understand and assert its structure.
Stability :
Musks are very stable, as in alcoholic and in functional fragrances
Uses in perfumery :
Muscone® is used in fine fragrance for musky, floral and animalic notes and in reproductions of natural musk.
Gives an interesting powdery-violet effect in leather and woody perfumes.
Year of discovery :
Discovered in 1905 but the molecular structure was first identified in 1925.
Isomerism :
This compound has an asymmetric carbon that gives rise to two possible enantiomers with a similar smell. There is also a molecule called Nor-Muscone® (or Exaltone), which has no branching. Its smell is roughly equivalent to classic Muscone®.
Synthesis precursor :
Muscone® is not a precursor to the synthesis of another compound of olfactory interest.
Natural availability :
Muscone® was originally found in natural musk, extracted from the Tibetan goat. Nowadays, only synthetic Muscone® is produced.
Synthesis route :
Muscone® is a macrocyclic musk that can be synthesized in many ways. One of them is from Citronellal to synthesize diacetyldodecane, which is the widespread method. This compound is cyclized by a ruthenium catalysis, followed by a catalytic hydrogenation to obtain the final Muscone®.
Regulations & IFRA
This ingredient is not restricted

