Lilial®
Lysmeral® ; Lilialdéhyde ; Lilestralis® ; Lilyall® ; 3-(4-tert-butylphenyl)butanal ; Aldehyde MBDC ; 2-(4-tert-butyl benzyl) propionaldehyde ; Butyl phenyl methyl propional ; Para-tert-butyl-alpha-methyl hydrocinnamaldehyde ; Para-tert-butyl-alpha-methyl hydrocinnamic aldehyde ; 3-(4-tert-butylphenyl)butanal ; Butylphenylmethylpropional ; Liligul N 743 CLP ; Lilyall ; Mefloral ; Alpha-methyl-beta-(para-tert-butylphenyl)propionaldehyde
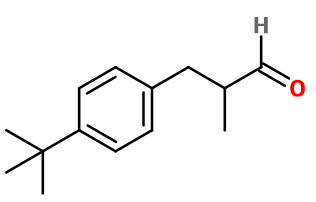
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 80-54-6
-
EINECS number : 201-289-8
-
FEMA number : Donnée indisponible.
-
Density : 0,939
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Heart/Base
-
Price Range : €€
-
Appearance : Colorless liquid
-
FLAVIS number : Donnée indisponible.
-
JECFA number : Donnée indisponible.
Information on synthetic ingredients
-
Acid Value : Lorem Ipsum
-
Boiling Point : 279°C
-
Detection Threshold : 0,27 ng/l air
-
Molecular formula : C14H20O
-
Log P : 4,2
-
Molecular Weight : 204,31 g/mol
-
Fusion Point : -20°C
-
Flash Point : 79°C
-
Vapor pressure : Lorem Ipsum
Uses
Other comments :
Very close to Lyral®. Lilial® is more stable than Cyclamen Aldehyde, for a similar synthetic route.
Lilial® is one of the 26 allergens in perfumery.
Stability :
Very unstable in various functional bases.
Aldehydes may form diethylacetals in alcoholic perfumes, with no real impact on their smell.
Most of the time, the occurrence of a benzenic cycle in a molecule causes a coloration of this molecule through time.
Uses in perfumery :
Lilial® is used in all types of perfumes to give heart to a jasmine, freesia, cyclamen, lotus, lily of the valley or lilac accord.
Year of discovery :
Discovered in 1956. Patent N°2,875,131 published in June, 11 1956 by Carpenter.M, Nutley, Easter W.Jr, Hasbrouck Heights for Givaudan Corporation
Isomerism :
Lilial® has an asymmetric carbon, giving rise to two possible enantiomers. These two isomers have a similar smell close to lily of the valley.
Synthesis precursor :
Lilial® forms a Schiff base with amines such as Methyl Anthranilate or Indole.
Natural availability :
Lilial® is not available in its natural state.
Synthesis route :
Lilial® is prepared in the same way as Cyclamen Aldehyde : a condensation of tert-butylbenzaldehyde (unlike isopropylbenzaldehyde) with propanal, followed by a catalytic hydrogenation of the compound obtained, allows to obtain Lilial®. Another synthetic route exists and consists in a catalytic hydrogenation of alpha-MethylCinnamaldehyde to obtain alpha-methyldihydroCinnamyl Alcohol. Following this first step, an alkylation using tert-butyl chloride or isobutene is operated to obtain a third reaction intermediate, then dehydrogenated to obtain Lilial®.
Regulations & IFRA
-
IFRA 51th : This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
-
Restriction type : RESTRICTION_PROHIBITION
-
Cause of restriction : DERMAL SENSITIZATION AND SYSTEMIC TOXICITY
-
Amendment : 49
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A Cat.5B Cat.5C Cat.5D Cat.6 Prohibited 0,09 % 0,04 % 1,4 % 0,06 % 0,05 % 0,05 % 0,017 % Prohibited Cat.7A Cat.7B Cat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A Cat.10B Cat.11A Cat.11B Cat.12 0,04 % 0,04 % 0,017 % 0,1 % 0,1 % 0,63 % 0,017 % 0,017 % 16 %
Comments :
p-tert-Butyl-α-methylhydrocinnamic aldehyde (p-BMHCA) should not be used for any finished product application included under IFRA Categories 1 and 6 (lipsticks and oral care products). This ingredient is part of the Schiff base (Lysmeral-methyl anthranilate (or Verdantiol) - N°CAS : 91-51-0) and induces the application of IFRA regulations for 60,6% of the Schiff base usage. Please also refer to the IFRA Annex II for more information

