| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Naturality | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | Certifications | Comments | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Beurre d'Iris 15 % d'Irones - 30 gr | - | - | - | - | - | - | more | - | |
|
|
ORRIS Butter (Essential oil) | M_0040043 | Naturel | - | - | - | - | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS 10% IRONE | E2515 | Beurre | - | Iris pallida Lam. / Iris germanica L. | Rhizome | Asie, Europe, France, Maroc | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS 70%/MPG | E2445 | Résinoide | - | Iris germanica L. | Rhizome | Maroc | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS ENZYMATIC 20% IRONE | F3507 | Huile essentielle | - | Iris pallida Lam. | Rhizome | France | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS LANDES 10% IRONE | E2514A | Beurre | - | Iris pallida Lam. | Rhizome | France | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS LANDES 15% IRONE | E2512A | Beurre | - | Iris pallida Lam. | Rhizome | France | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS LANDES 20% IRONE | E2511A | Beurre | - | Iris pallida Lam. | Rhizome | France | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS LANDES 68% IRONE | E2468 | Absolue | - | Iris pallida Lam. | Rhizome | France | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS LANDES 8% IRONE | E2513A | Beurre | - | Iris pallida Lam. | Rhizome | France | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS LANDES 80% IRONE | E2464A | Absolue | - | Iris pallida Lam. | Rhizome | France | more | - | |
|
|
IRIS LAVE | F1523 | Résinoide | - | Iris germanica L. | Rhizome | Maroc | more | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 8002-73-1
-
EINECS number : 285-368-2
-
FEMA number : 2829
-
Density :
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Heart/Base
-
Price Range : €€€€€
-
Appearance : Whitish wax
Uses
Other comments :
The price of orris root butter (and absolute) depends greatly on its rate of Irone. This price is around 12 000 € / kg for butter and can go up to 40 000 € / kg for the absolute. It is historically one of the most expensive and most coveted raw material of perfumery.
Natural Irones (alpha-irone, beta, gamma) can be obtained from the butter or the absolute. The synthesis of these molecules is preferred for cost reasons.
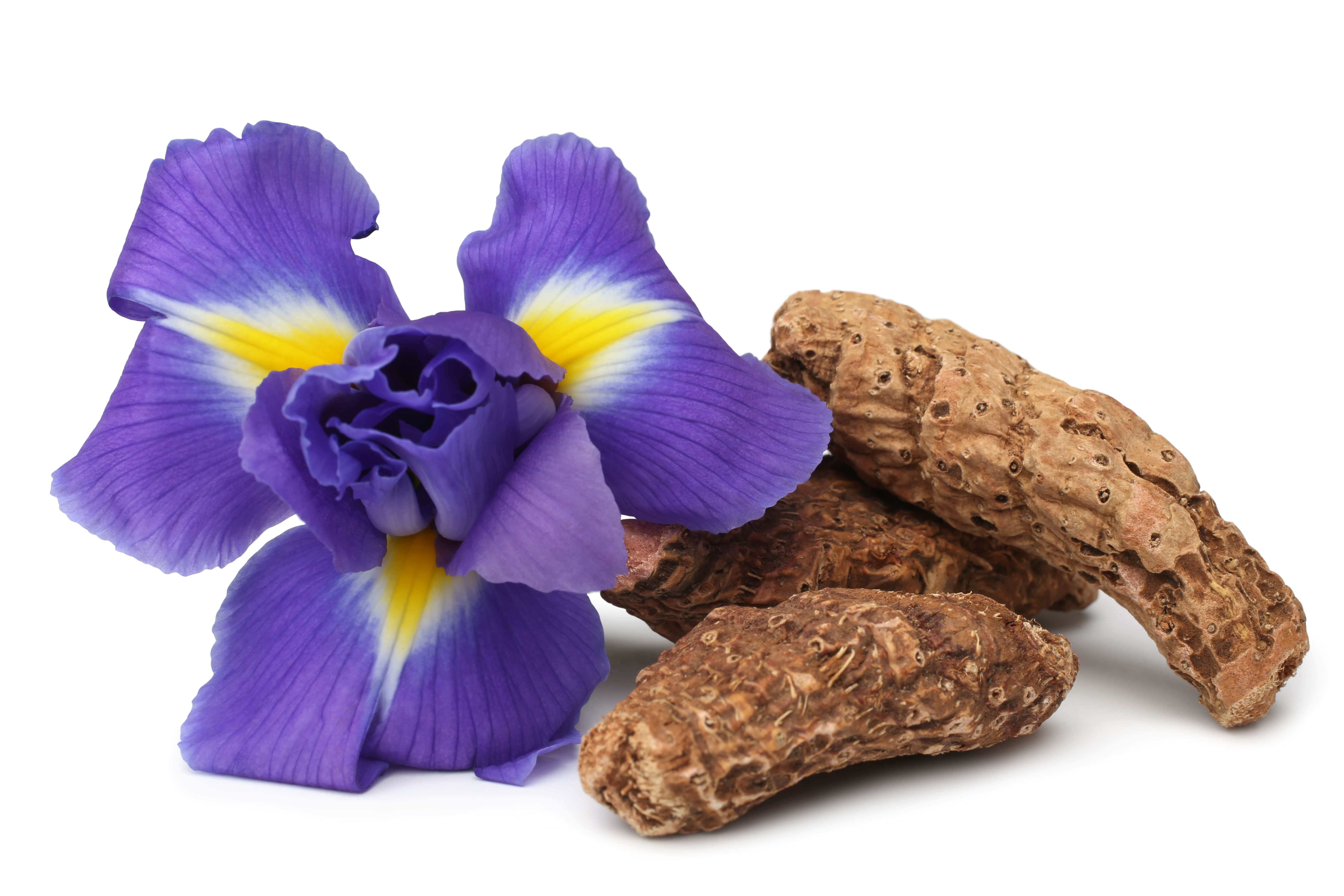
The term ''iris '' means ''rainbow '' in Greek, illustrating the colour variety of the flowers found in this kind of plant.
The iris absolute can be favoured in a composition for its stability (it does not precipitate) and orris root butter for its price.
Between the 1970s and 2000, Iris crop has undergone a major crisis in terms of output volume. This led to a rarefaction of this product already considered noble. This crisis allowed the development of new production areas, almost non-existent until then, such as Morocco. Today, production has gradually returned to sufficient volumes to meet the needs of the perfumery industry, although Iris is still considered a premium product.
Orris is the iconic flower of Florence city so much that it appears on the city's coat of arms.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
Stable oil in perfumes and in diverse functional bases
Uses in perfumery :
Used in small quantities for sweet floral-violet notes but also with woody notes (sandalwood) and for green notes. Since 1850, the use of Iris Florentina declines in favour of Iris Pallida. Nowadays, Iris pallida is used more because its yield is better and its smell is more powdery and closer to violet. Since its introduction in perfumery with Vera Violeta- Roger & Gallet (1892), Iris has been the happiness of all perfumers. At once warm and dry, sensual and creamy, powdery and oily, its scent is unique. It can be found in many fragrances, and a large majority of niche ranges have an iris perfume. However, this scent is often reproduced because the price of Iris butter does not allow regular use.
Major Components :
- Myristic Acid (60-65%)
- cis-Irone-gamma (≈8%)
- Lauric Acid (≈7%)
- cis-Irone-alpha (≈6%)
- Palmitic Acid (≈3%)
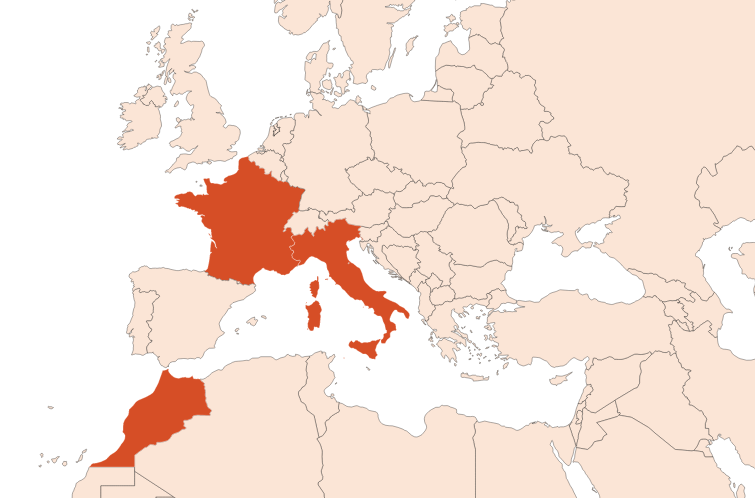
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Botanique :
The orris root belongs to a plant of the Iridaceae family, and of the genus Iris.
Chemotypes :
In perfumery, there are 2 main species of Iris:
Iris pallida, grown in Italy (Tuscany) primarily rich in cis-γ-irone, then cis-α-irone.
Iris germanica including the emblematic variety Iris germanica var. florentina (originally from Italy too), now cultivated in China, Morocco and India. It is mainly composed of cis-α-irone, followed by cis-γ-irone.
The difference between these two species is very simple: flowers are white for Iris florentina and blue for Iris pallida.
Extraction process :
The cultivation of Iris must be done on a well-drained rocky soil and requires a great sun exposure. The plant is grown for three years before its rhizome is harvested in January and February or July and August.
Today, iris harvesting is increasingly mechanized, allowing the rhizomes to be removed easily from the ground. After harvesting, iris rhizomes are trimmed and washed.
There are then several types of process before putting the rhizomes to dry. In some (rare) regions of the world such as Tuscany or a little in Morocco, the rhizomes are peeled and cleaned after harvesting (this is called ''white '' iris). This process is complex because it cannot be mechanized and must be done by hand. It does, however, result in a much better olfactory quality. The huge majority of global production does not undergo this process and is ''simply '' sliced mechanically (known as ''black '' iris).
Whatever the process, they are then left to dry in the sun for several days. At this stage, the rhizomes are still almost odorless. This drying is essential because it determines the degree of maturation of the rhizomes, an important factor in the rate of transformation of irone, itself a factor in the olfactory quality of the butter or Iris absolute.
Three more years of drying then follow, during which the rhizome synthesizes molecules called irones, chemically close to ionones. This step is crucial to obtain the olfactory quality of the root.
(A bacterial treatment can accelerate the maturation of the roots from three years to just a few days! However, the treatment has a negative impact on the olfactory quality of the root).
Rhizomes are then powdered and undergo molecular hydrodistillation (under 0.5 to 1.5 bar pressure and for about 15 hours), to obtain a Iris Butter (concrete) with a yield of about 0.2%. This butter can then undergo fractional distillation to obtain Iris Absolute with a yield of about 0.04% from the rhizomes. Iris powder can also be treated directly with volatile solvents to obtain Iris Resinoid with a yield of about 3 to 4%. These yields as well as the time required for production explain the cost of this raw material.
In terms of production, the concrete that is preferred, about 200kg are produced each year, containing about 10-20% irone, sold at approx. 10k€/Kg. Only a few kilos of Absolute d'Iris are produced, containing more than 60% irone, sold at approx. 50k€/Kg. Resinoid is not much produced.
Geographic origin :
Data not available.
Regulations & IFRA
This ingredient is not restricted

