| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Comments | Naturality | Certifications | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Absolue de Ciste - 30 gr | - |
Visit website
|
- | - | - | - | - | - | |
|
|
CISTE | F0779 |
Visit website
|
Absolue | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | - | |
|
|
CISTE | F0850 |
Visit website
|
Concrète | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | - | |
|
|
CISTE | F0940 |
Visit website
|
Eau concentrée | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | - | |
|
|
CISTE 70%/TEC | E1264 |
Visit website
|
Absolue | - | Cistus ladaniferus L. | Feuille, Rameau | Espagne | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : 8016-26-0
-
EINECS number : 934-780-7
-
FEMA number : 2608
-
Appearance : Brown resin
-
Density :
-
Volatility : Base
-
Price Range : Donnée indisponible.
Physico-chemical properties
-
Optical rotation : Donnée indisponible
-
Vapor pressure : Donnée indisponible
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Donnée indisponible
-
Acid Value :
-
Flash Point :
Uses
Uses in perfumery :
Data not available.
Major Components :
Data not available.
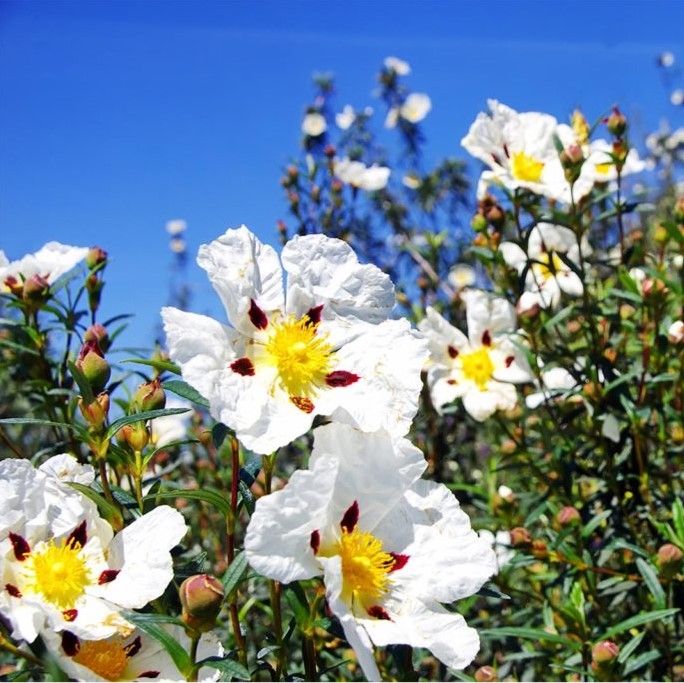
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Botanical name :
Cistus ladanifer L.
Synonyms : Cistus ladaniferus L. // Cistus ladanifer f. immaculatus Dans.
Botanical profile :
The cistus belongs to the Cistaceae family and to the genus Cistus.
Chemotypes :
The genus Cistus includes about 20 different species, the majority of which exudes fragrant gum.
Among these, the most used are:
Cistus ladaniferus var. albiflorus, var. maculatos, var. stenoiphyllus, which produce the resin used in perfumes.
Cistus creticus, with rose to purple petals, surronding a tuft of stamens.
Cistus salvifolius, with white petals.
Cistus parviflorus, with pale rose petals.
Extraction process :
In April, Cistus ladaniferus fields are covered with the famous white flowers, but they don't smell and are very delicate (they only last a few days). It is necessary to wait a few months, around May-June, for a new shoot to appear. This new branch protects itself from the sun - and from the summer heat of southern Spain - by secreting a very fragrant viscous gum. We use the latter in perfumery.
In July, from dawn to noon, new branches are cut with a sickle, bundled and taken to the factory to extract the gum. It will then be necessary to wait another 3 years to harvest the cistus again.
To obtain the resinoid, the gum is treated in a soda solution for extraction with a 3 to 5% yield. After filtration, an acid treatment is carried out. A pasty product is recovered by skimming and distilled to dry it. The paste is finally treated with alcohol, then filtered to remove insoluble compounds. A ''labdanum alcohol resinoid '' is then obtained.
Several reprocessing are possible on the cistus absolute, to remove insoluble compounds or colour. Such rectification has no olfactory impact.
Other comments :
Data not available.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized
Regulations & IFRA
Allergens :
This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
IFRA 51th :
This ingredient is restricted by the 51th amendment
Annexe I :
Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Cinnamic alcohol | 104-54-1 | 0,03 |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,6 |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,6 |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,9 |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,38 |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,2 |
| l-Carvone | 6485-40-1 | 0,6 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,06 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,4 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 0,5 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,01 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,12 |
| Methyl eugenol | 93-15-2 | 0,05 |
| Isophorone | 78-59-1 | 0,2 |
| Carvone | 99-49-0 | 0,25 |

