| Company | Ingredient Name | ID | Naturality | Purity | Latin name | Treated part | Geographical origin | Certifications | Comments | MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Absolue de Castoreum - 30 Gr | - | - | - | - | - | - | more | - |
General Presentation
-
CAS N° : : 8023-83-4
-
EINECS number : 232-427-5
-
FEMA number : 2261
-
Density :
-
Optical rotation : Lorem Ipsum
-
Allergens : This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
-
Refractive Index @20°C : Lorem Ipsum
-
Volatility : Base
-
Price Range : €€€€
-
Appearance : Brown paste
Uses
Other comments :
In the state of Ontario, in Canada, a trapper can receive $ 10 to $ 40 for bringing a pouch containing the substance to the Ontario Trappers Association.
Nowadays, the use of castoreum in perfumery is very regulated, this raw material tends to be replaced by the internal bases of the perfumery companies.
Stability :
Solubility issues in perfumes
Stable oil in perfumes and in diverse functional bases
Uses in perfumery :
Useful in oriental, chypre and leather fragrances. Gives power, strength and tenacity. To be associated with certain flowers such as Tuberose Absolute.
Major Components :
- Benzoic Acid
- Gaiacol
- Créosol
- Castorine
- Cinnamic Acid
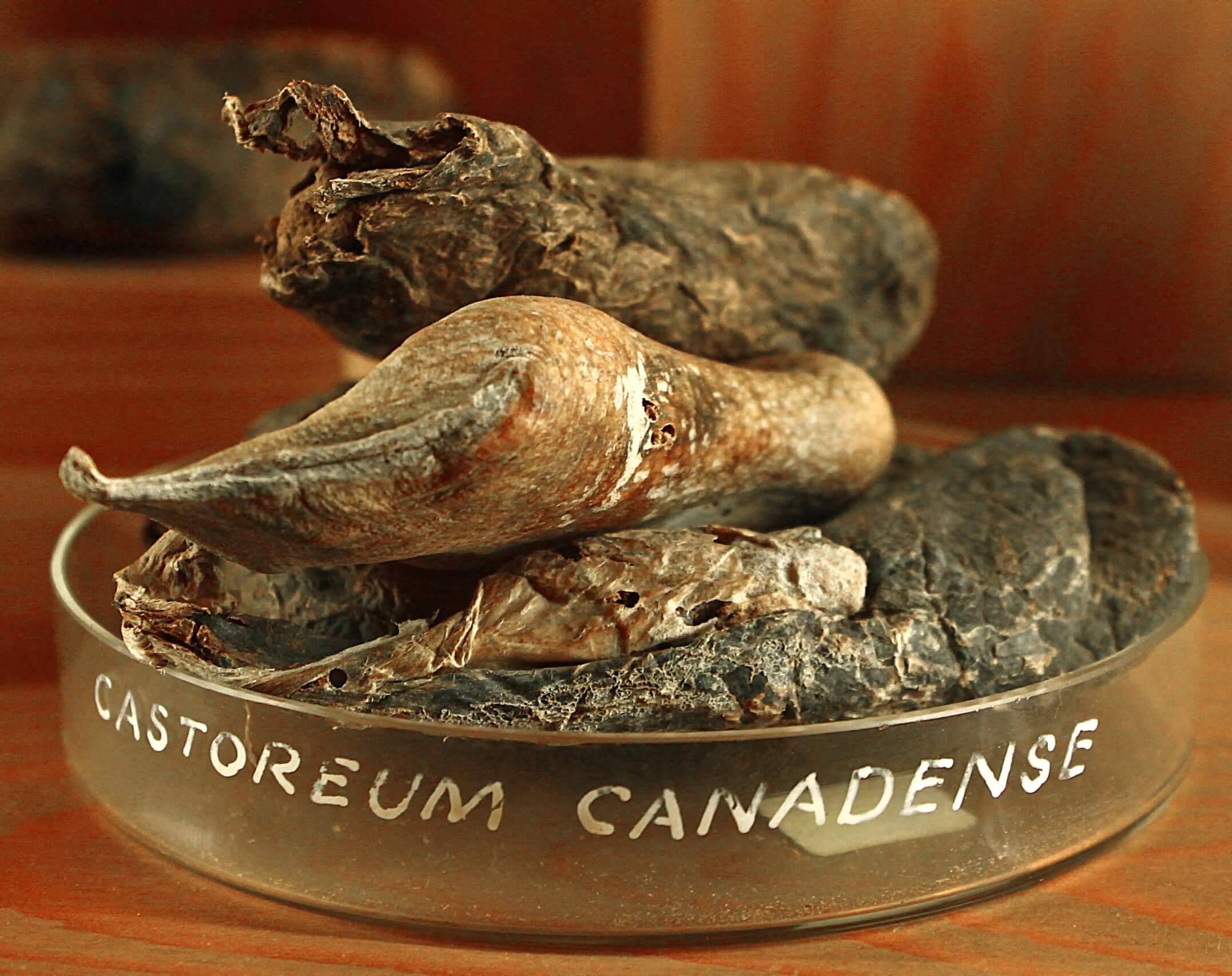
Photo credits: ScenTree SAS
Botanique :
The beaver is an animal of the Castoridae family and of the genus Castor.
Chemotypes :
The Siberian castoreum pocket quality is known to be better than the Canadian one.
Extraction process :
Castoreum results from the extraction of a secretion located in the pocket of the American or European beaver, located near its anus. The beaver uses this secretion, in combination with its urine, to mark its territory and coat himself with an impervious layer to dive into the water. This pocket is both present in the male and the female. The beaver must be killed in order to collect the secretion pocket.
The resinoid results from drying the pocket for one to two years, grinding and then dyeing it in the alcohol. This dyeing is generally carried out by mixing about 20 parts of alcohol by weight depending on the mass of the bags. A small amount of potash can be added to promote the extraction. The overall yield of the extraction is relatively high: 45 to 75% castorum resin is soluble in alcohol.
Sometimes, the pockets drying is done with the smoke of a wood fire. This practice gives the extract a smokier and more violent smell, bringing it closer to the birch tar note.
The castoreum resinoid can be distilled to be bleached, without a great olfactory deterioration.
Geographic origin :
Data not available.
Regulations & IFRA
This ingredient is not restricted


